After a tough workout, your body needs the right nutrients to bounce back. Soreness and fatigue can slow you down, but eating the right ingredients can speed up the process. Certain choices are packed with anti-inflammatory properties, aiding in faster healing.
Science supports specific options to reduce discomfort and repair tissues. Alongside rest and hydration, these picks optimize performance. Whether you’re an athlete or a weekend warrior, fueling properly makes a difference.
Key Takeaways
- Nutrition plays a vital role in easing post-exercise discomfort.
- Anti-inflammatory compounds in certain items promote faster healing.
- Combining smart eating with rest boosts results.
- Hydration and stretching complement dietary efforts.
- Targeted choices can shorten downtime between sessions.
Understanding Muscle Soreness and Recovery
Ever wondered why your body feels tender post-workout? That stiffness, known as DOMS (Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness), peaks 24–72 hours after exercise. It’s your body’s way of signaling repair.
What Causes Post-Workout Soreness?
DOMS results from microscopic tears in fibers during intense activity. Inflammation follows as a natural healing response, but it also brings stiffness. Oxidative stress worsens discomfort by damaging cells further.
How Nutrition Accelerates Recovery
Eating right reduces downtime. Protein provides amino acids to rebuild fibers, while carbs refuel energy stores. Kimberly Collins, a sports nutritionist, emphasizes their synergy:
“30g protein post-workout paired with carbs optimizes repair.”
| Nutrient | Role | Best Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Repairs muscle damage | Eggs, whey, fish |
| Carbs | Restores glycogen | Sweet potatoes, oats |
| Omega-3s | Fights inflammation | Salmon, chia seeds |
Avoid added sugars and alcohol—they spike inflammation. Hydration and sleep further enhance results.
Tart Cherry Juice: A Powerhouse for Muscle Repair
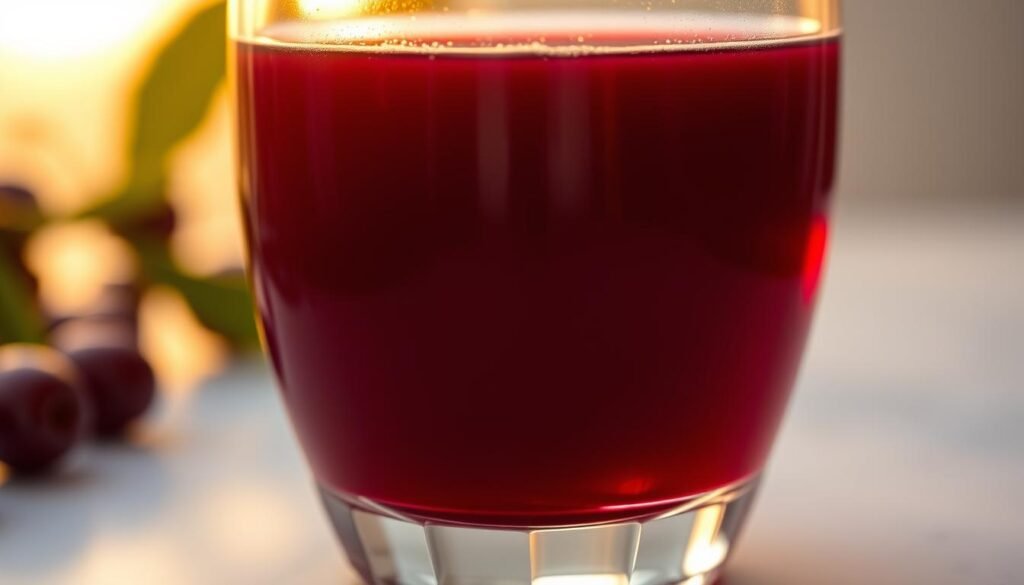

Science backs tart cherry juice as a game-changer for post-exercise stiffness. Its deep red hue signals high levels of anthocyanins, compounds that reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. A 2021 meta-analysis of 15 studies confirmed it accelerates healing after intense sessions.
Anthocyanins and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects
These pigments do double duty:
- Neutralize free radicals to protect cells.
- Block enzymes that trigger swelling and soreness.
Athletes drinking 8–16 oz daily saw37% less DOMSin trials. Enriched versions may offer higher potency, but natural options work well too.
Optimal Timing for Consumption
Start 3–4 days before heavy training for best results. Post-workout, blend it into smoothies or take a quick shot. Consistency matters—effects peak after 8–10 days of use.
| Type | Anthocyanin Content | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Natural | Moderate | Daily use |
| Enriched | High | Pre-competition |
Pair it with protein to maximize muscle damage repair. Avoid sugary mixes—they undermine the anti-inflammatory benefits.
Fatty Fish: Omega-3s to Combat Inflammation
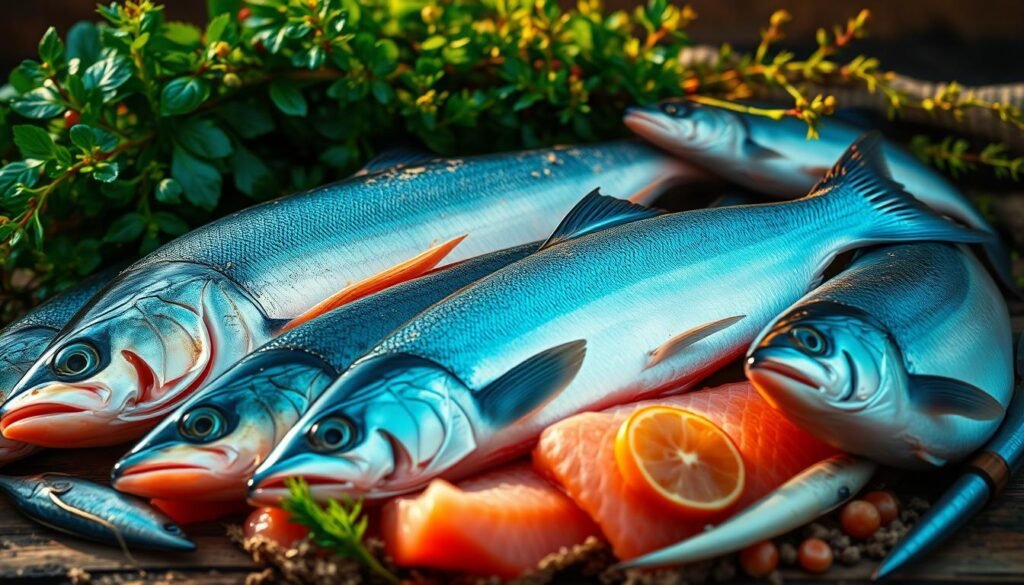

Fatty fish delivers a one-two punch of essential nutrients for faster healing. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids and high-quality protein, options like salmon and sardines tackle soreness and repair tissues simultaneously. Research shows 1.8–3g of omega-3s post-workout can reduce DOMS by up to 30%.
Best Fish Choices for Recovery
Not all seafood is equal. Prioritize these omega-3-rich varieties:
- Salmon (29g protein per 4 oz serving)
- Mackerel (highest EPA/DHA concentration)
- Sardines (budget-friendly and portable)
Their EPA and DHA compounds directly dampen inflammatory cytokines, speeding up recovery.
Protein and Healthy Fats Synergy
The amino acids in fish rebuild fibers, while fats enhance nutrient absorption. Pair grilled salmon with quinoa or spinach to boost iron uptake for oxygen delivery. Avoid fried preparations—they negate anti-inflammatory benefits.
“Omega-3s from fish oil outperform supplements for reducing exercise-induced inflammation.”
Watermelon and Its Hydrating Benefits
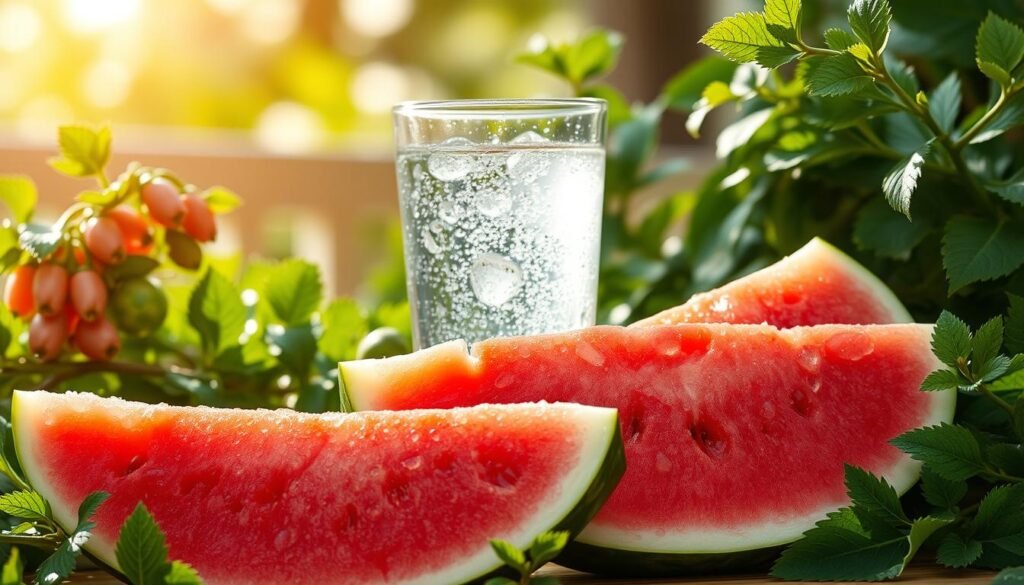

Few summer treats double as powerful recovery aids like watermelon. Its 92% water content replenishes fluids lost during exercise, while electrolytes like potassium prevent cramps. A 2013 study found 500mL of its juice reduced soreness 24 hours post-workout.
L-Citrulline for Nitric Oxide Boost
This fruit contains L-citrulline, an amino acid that converts to arginine in your body. The process boosts nitric oxide production, widening blood vessels for better nutrient delivery to tired tissues. Enriched juices may offer higher doses, but natural options provide balanced benefits.
Antioxidants to Reduce Oxidative Stress
Watermelon’s pink flesh packs antioxidants like lycopene and vitamin C. They neutralize free radicals, which spike after intense sessions. Pair it with mint or feta for a post-workout snack that fights inflammation:
- Watermelon-feta salad: Adds protein and healthy fats.
- Blended juice with mint: Enhances digestion and freshness.
“L-citrulline from watermelon improves blood flow more effectively than synthetic supplements in athletes.”
Pomegranate Juice: Polyphenol-Rich Recovery Aid
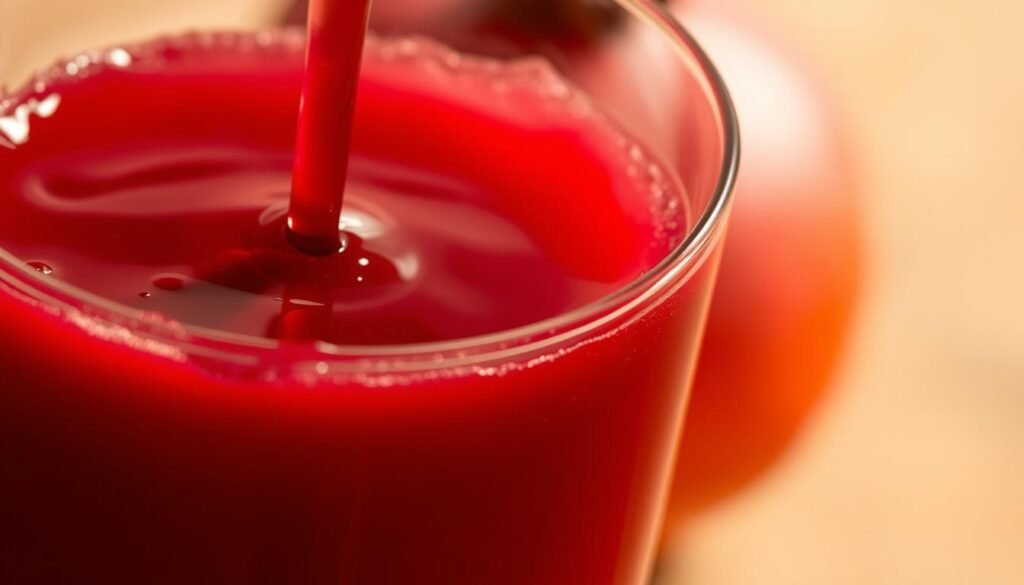

Bright red and bursting with benefits, pomegranate juice stands out as a recovery superstar. Its high concentration of polyphenols, especially punicalagins, tackles post-exercise stress like few other drinks can. A 2017 study found it lowered MDA, a key marker of oxidative damage, in weightlifters by 27%.
Reducing Oxidative Damage Post-Workout
Punicalagins in pomegranate juice neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from further harm. These compounds also enhance blood flow, delivering nutrients to tired tissues faster. For endurance athletes, 8 oz daily before training can significantly cut downtime.
Pair it with Greek yogurt for a protein-polyphenol combo that maximizes repair. The probiotics in yogurt further support gut health, which is linked to reduced inflammation. Avoid commercial brands with added sugars—they dilute the juice’s natural antioxidants.
“Phytochemicals in pomegranate juice not only ease soreness but also bolster immune function during intense training cycles.”
Beetroot Juice: Nitrates for Enhanced Blood Flow
Deep crimson and packed with performance perks, beetroot juice is a natural powerhouse for athletes. Its high nitrate content converts to nitric oxide, widening blood vessels to deliver oxygen faster to fatigued tissues. A 2016 study showed it cut soreness by 19% 48 hours post-exercise.
How Nitrates Boost Oxygen Delivery
Nitrates in beetroot juice transform into nitric oxide, enhancing blood flow during workouts. This process reduces oxygen demand, letting you train harder with less strain. For best results, drink 8–12 oz 2–3 hours before exercise.
Betalains and Cellular Energy Efficiency
The juice’s betalains do double duty: they’re antioxidants that reduce inflammation and improve mitochondrial efficiency. This means your cells produce energy more effectively, speeding up repair. Pair it with citrus (like orange slices) to amplify nitrate absorption.
“Soccer players drinking beetroot juice pre-game reported 22% less DOMS post-match, per a 2021 study.”
Skip processed versions with added sugars—they dilute the benefits. Fresh or cold-pressed options offer the highest nitrate concentration for optimal recovery.
Whey Protein: Fast-Acting Muscle Builder
When it comes to rapid post-workout repair, few options match the efficiency of whey protein. Derived from milk, it’s packed with essential amino acids, including leucine, which triggers tissue synthesis. Studies show it reduces damage markers faster than plant-based alternatives, making it a staple for athletes.
Why Whey Outshines Other Proteins
Speed matters after exercise. Whey absorbs quicker than pea or soy, delivering nutrients when your body needs them most. Key advantages:
- 20–40g post-workout with carbs (like a banana smoothie) optimizes repair.
- Hydrolyzed versions suit lactose-sensitive individuals without sacrificing benefits.
- Complete amino acid profile supports full recovery cycles.
| Type | Absorption Speed | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Whey Isolate | Fastest (30 mins) | Post-workout |
| Plant-Based | Slower (2+ hours) | Meal replacement |
While convenient, don’t rely solely on supplements. Whole-food sources like eggs or fish offer complementary nutrients. Balance is key for long-term results.
“Whey’s leucine content stimulates muscle synthesis 25% more effectively than plant proteins.”
Eggs: Nutrient-Dense Recovery Fuel
Eggs pack a powerful punch when it comes to post-exercise repair. They’re loaded with high-quality protein and essential nutrients, making them a top choice for athletes. Research shows whole eggs outperform egg whites for muscle growth, thanks to the yolk’s rich profile.
The Whole Egg Advantage
Discarding the yolk means missing out on key vitamins and minerals. A 2017 study found whole eggs boosted muscle synthesis 40% more than egg whites alone. The yolk delivers:
- Vitamin D: Supports calcium absorption for bone strength.
- Choline: Aids nerve function and reduces inflammation.
- Omega-3s: Combat post-workout soreness.
Debunking Cholesterol Myths
Fear of dietary cholesterol is outdated. For active individuals, eggs’ amino acids far outweigh risks. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition notes:
“Egg consumption doesn’t raise heart disease risk in athletes—it enhances recovery.”
Pair eggs with spinach to boost iron absorption or avocado for healthy fats. Try a post-workout veggie omelet or scrambled eggs on whole-grain toast for balanced recovery.
Beyond Food: Additional Recovery Strategies
Nutrition is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to bouncing back after intense exercise. Combining smart eating with other proven methods can maximize your results and reduce downtime. Here’s how to enhance your routine beyond the plate.
Sleep: The Ultimate Repair Tool
Quality sleep is non-negotiable for repair. During deep sleep, your body releases growth hormone, which fuels tissue regeneration. Aim for 7–9 hours nightly to optimize protein synthesis and reduce DOMS.
Key benefits of proper rest:
- Repairs microtears in fibers more efficiently.
- Balances cortisol levels to lower inflammation.
- Enhances memory consolidation for skill-based training.
Compression Therapy: Science-Backed Support
Compression garments aren’t just trendy—they work. Studies show they improve recovery by 37% by enhancing blood flow and reducing swelling. Options vary:
| Type | Best For | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic Devices | Post-competition | High (professional settings) |
| Sleeves/Socks | Daily use | Moderate (accessible) |
Wear them 2–4 hours post-workout for best results. Pair with elevation to further reduce soreness.
Foam Rolling and Massage Techniques
Self-myofascial release breaks up knots and improves mobility. A 2019 study found foam rolling boosted performance by 15% when done post-exercise. Target major groups:
- Quadriceps: Roll slowly from knee to hip.
- Hamstrings: Pause on tender spots for 20–30 seconds.
- Calves: Cross one leg over the other for deeper pressure.
For deeper relief, try contrast showers—alternate 1 minute hot (104°F) with 30 seconds cold (60°F). This reduces muscle soreness by flushing metabolic waste.
“Professional athletes using massage therapy saw 23% faster strength recovery versus passive rest.”
Conclusion
Optimizing post-exercise repair starts with smart choices. Tart cherry juice fights inflammation, fatty fish delivers omega-3s, and beetroot juice boosts blood flow. Each option targets soreness differently but works best when combined.
Don’t overlook hydration, sleep, and active recovery. These elements work with nutrients to speed up healing. Avoid alcohol and processed items—they slow progress.
Ready to test these strategies? Try the salmon-sweet potato combo from our first source. It’s packed with protein and carbs to reduce muscle soreness effectively.
Your next workout doesn’t have to leave you sidelined. Small tweaks make big differences in how you feel and perform.

